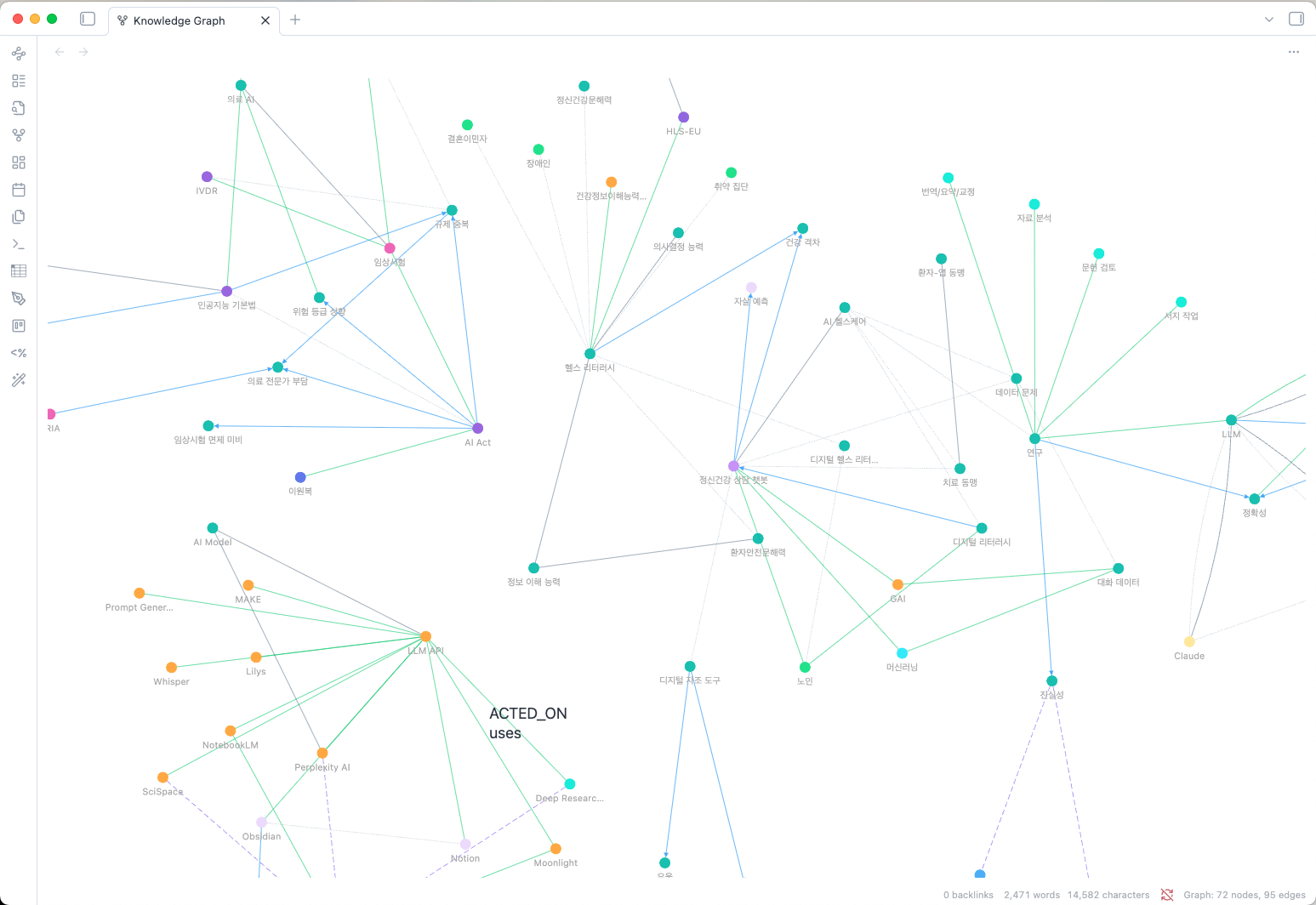
This plugin builds a lightweight knowledge graph from users' Obsidian notes using LLM-powered entity extraction with a simple yet expressive ontology model to provide knowledge extraction, exploration, and RAG search. Since Obsidian provides wonderful links between notes, implementing ontology model would meet users' (especially researchers') needs.
Traditional knowledge graphs often require complex schemas with dozens of entity and relationship types, making them difficult to maintain and query. Simple Graph Builder takes a different approach:
- 10 Fixed Entity Types: PERSON, ORGANIZATION, CONCEPT, PROJECT, TOOL, EVENT, PLACE, DOCUMENT, METHOD, TOPIC - covering all common knowledge domains
- Free-form Relationship Verbs: Express relationships naturally with active verbs like "develops", "uses", "causes", "cites"
- Detail Property: Each relationship includes a
detailfield for nuanced descriptions without schema explosion
This design provides structured entity classification with expressive relationships, making it easy to build, query, and maintain your personal knowledge graph.
- Lightweight Ontology Model: Simple but expressive - 10 fixed entity types + free-form relationship verbs with detail annotations
- Hybrid Entity Resolution: Multi-stage deduplication pipeline combining fast lookups with embedding similarity and LLM verification (inspired by KGGen [3])
- Smart Search: AI-powered natural language queries over your knowledge graph with multi-path exploration
- Entity Extraction: Automatically extract entities from your notes using AI (configurable extraction depth)
- Internal Link Support: Automatically processes
[[wikilinks]]to build note-to-note connections - Multiple LLM Support: Works with Claude, OpenAI, Gemini, and Ollama (local)
- Korean Language Support: Bigram Jaccard similarity for robust Korean text matching (handles particles and spacing variations)
- Interactive Graph View: Visualize your knowledge graph with fCoSE force-directed layout
- Large Graph Support: Optimized for thousands of nodes with fast rendering
- Note Neighborhood Panel: See connections for the current note in a sidebar
- Manual Entity Merge: Merge duplicate entities via graph view context menu
- Quick Access: Ribbon icon menu for common actions
- Status Bar: Real-time graph statistics display
A key insight from recent knowledge graph research is that entity resolution is critical for quality knowledge graphs [3]. Without proper deduplication, "AI", "artificial intelligence", and "Artificial Intelligence" appear as separate nodes, fragmenting your knowledge.
Simple Graph Builder uses a hybrid resolution pipeline (opt-in feature):
| Stage | Method | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Persistent cache | Previously resolved tokens | O(1) |
| 2. Session cache | Same name resolved this session | O(1) |
| 3. Exact name | Hash lookup on canonical name | O(1) |
| 4. Alias match | Hash lookup on stored aliases | O(1) |
| 5. Embedding similarity | Cosine similarity > 0.90 = auto-merge | O(n) |
| 6. LLM verification | Ambiguous matches (0.80-0.90) verified by LLM | API call |
| 7. Create new | No match found | - |
This approach resolves most entities via fast hash lookups, reserving expensive embedding searches and LLM calls for genuinely ambiguous cases.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Analyze current note |
Extract entities from the active note |
Search related notes |
Find notes by entity name (exact/fuzzy match) |
Smart Search (AI) |
Natural language search using LLM to explore the graph |
Open graph view |
Show the knowledge graph visualization |
Open note neighborhood panel |
Show current note's connections in sidebar |
Remove current note from graph |
Remove active note from the graph |
Clear all graph data |
Reset the entire graph |
The LLM must classify each entity into one of these types:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
PERSON |
People, individuals | Authors, researchers, team members |
ORGANIZATION |
Companies, institutions | Google, MIT, research labs |
CONCEPT |
Ideas, theories, principles | Machine learning, API design |
PROJECT |
Projects, products, initiatives | Obsidian, GraphRAG |
TOOL |
Software, hardware, instruments | Python, VS Code, Docker |
EVENT |
Meetings, conferences, milestones | NeurIPS 2024, sprint review |
PLACE |
Locations, venues, geography | San Francisco, AWS us-east-1 |
DOCUMENT |
Papers, books, articles, notes | "Attention Is All You Need" |
METHOD |
Techniques, approaches, workflows | Agile, TDD, fine-tuning |
TOPIC |
Subjects, themes, fields, domains | NLP, distributed systems |
Relationships are expressed as active verbs describing how entities relate:
| Verb Examples | Meaning |
|---|---|
develops, creates, builds |
Creation, authorship |
uses, applies, implements |
Usage, application |
causes, leads to, enables |
Causality, dependency |
contains, includes, has |
Composition, membership |
cites, references, based on |
Citation, source |
relates to, similar to |
General association |
Each relationship also includes an optional detail field for additional context.
Click the graph icon in the left ribbon to access:
- Analyze current note
- Open graph view
Shows real-time graph statistics with node counts by label.
A sidebar panel showing:
- Extracted Nodes: Entities from the current note with entity type badges
- Connected Nodes: Grouped by entity type (PERSON, CONCEPT, TOOL, etc.)
- Relationships: Shows relationship verb and detail for each connection
- Click nodes to see source notes and relationship details
Right-click a node to:
- Merge into...: Manually merge duplicate entities (source becomes alias of target)
- API Provider: Choose between Claude, OpenAI, Gemini, or Ollama
- API Key: Your API key (not needed for Ollama)
- Model: Select or enter a custom model name
- Extraction Mode: Control extraction depth
- Standard: Max 15 entities per chunk (fast, low cost)
- Thorough: No limits per chunk (comprehensive extraction)
- Chunked Processing: Long notes are automatically split into ~500 token chunks and processed in parallel (max 3 concurrent)
- Auto-analyze on save: Automatically analyze notes when you save them (2-second debounce)
- Analyze entire vault: Batch analyze all notes with progress tracking and cancellation support
You can configure a separate model for Smart Search queries, allowing you to use faster/cheaper models for extraction while using more capable models for search:
- Use separate model for smart search: Enable to configure a different model
- Smart search provider: Choose provider (Claude, OpenAI, Gemini, Ollama)
- Smart search model: Select or enter a custom model name
This is useful for optimizing cost vs. quality - e.g., use GPT-4o-mini for extraction and GPT-4o for search.
Enable embedding-based entity resolution for intelligent deduplication:
- Enable embeddings: Turn on the hybrid resolution pipeline
- Embedding provider: OpenAI, Gemini, or Ollama (can differ from main LLM provider)
- Embedding API key: Separate key for embedding API calls
- Embedding model:
- OpenAI:
text-embedding-3-small(1536 dims),text-embedding-3-large(3072 dims) - Gemini:
text-embedding-004(768 dims) - Ollama:
nomic-embed-text(768 dims),mxbai-embed-large(1024 dims)
- OpenAI:
- High confidence threshold: Auto-merge above this similarity (default: 0.90)
- Low confidence threshold: LLM verification range floor (default: 0.80)
- Enable LLM verification: Verify ambiguous matches with LLM calls
- Compute embeddings: Generate embeddings for existing nodes
- Clear resolution cache: Reset learned token mappings
- Open graph in main window: Toggle to open the graph visualization in a main tab instead of the right sidebar
- View graph statistics (nodes by entity type, total relationships)
- Clear all graph data
- Open Settings → Community plugins
- Search for "Simple Graph Builder"
- Click Install, then Enable
- Install BRAT from Community Plugins
- Open command palette → "BRAT: Add a beta plugin"
- Enter:
junhewk/simple-graph-builder - Enable the plugin in Settings → Community plugins
- Download
main.js,styles.css, andmanifest.jsonfrom the latest release - Create folder:
VaultFolder/.obsidian/plugins/simple-graph-builder/ - Copy the downloaded files into the folder
- Reload Obsidian and enable the plugin
- Configure your API key in Settings → Simple Graph Builder
- Open a note and run command:
Analyze current note - View results with command:
Open graph view
- Click a node to highlight its connections
- Double-click a node to open search with that term
- Right-click a node to access merge options
- Hover on edges to see relationship type and detail
- Click the background to reset highlights
- Scroll to zoom in/out
- Drag to pan around the graph
Node colors are determined by entity type (10 predefined colors). Edges use unified gray styling with relationship verbs shown on hover.
Two search modes are available:
- Run command:
Search related notes - Enter a concept or entity name
- Toggle Exact match for precise matching
- Click results to navigate to notes
- Run command:
Smart Search (AI) - Enter a natural language question (e.g., "What methods did we use for the recommendation project?")
- The LLM explores the graph using tool calls, following multiple paths
- View the AI-generated answer with relevant nodes and source notes
- Click source note links to navigate
Note: Smart Search requires models with tool calling support. Some Ollama models (deepseek-r1:*, gemma3:*) have limited support. Recommended: qwen3:*, gpt-oss:* for Ollama.
This plugin makes API calls to extract entities from your notes.
- Claude, OpenAI, Gemini: Each note analysis and Smart Search query will incur API costs based on your provider's pricing
- Ollama: Free (runs locally on your machine)
- OpenAI: ~$0.02 per 1M tokens for
text-embedding-3-small - Gemini: Free tier available for
text-embedding-004 - Ollama: Free (local models like
nomic-embed-text)
Consider using Ollama for cost-free operation, or batch analyze during off-peak hours to manage costs.
- Your notes are sent to the configured LLM provider for entity extraction
- No data is stored externally; all graph data stays in your vault
- Consider using Ollama for fully local, private processing
- Embeddings are stored locally in binary format (
embeddings.bin)
This plugin's entity resolution approach is inspired by recent advances in knowledge graph construction:
- LightRAG [1] demonstrated lightweight graph-based RAG but lacks entity resolution
- Microsoft GraphRAG [2] provides comprehensive extraction but at high cost ($50-100+ per corpus)
- KGGen [3] introduced the insight that entity resolution is critical for quality knowledge graphs
Simple Graph Builder combines the simplicity of LightRAG with KGGen's hybrid resolution approach, adapted for Obsidian's local-first architecture.
[1] Guo, Z., et al. (2024). "LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation." https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG
[2] Edge, D., et al. (2024). "From Local to Global: A Graph RAG Approach to Query-Focused Summarization." arXiv:2404.16130. https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag
[3] Shu, Y., et al. (2025). "KGGen: Extracting Knowledge Graphs from Plain Text with Language Models." NeurIPS 2025. arXiv:2502.09956. https://github.com/stair-lab/kggen
[4] Neo4j, Inc. (2024). "Neo4j GraphRAG Package for Python." https://neo4j.com/docs/neo4j-graphrag-python/current/
[5] Veen, A. (2024). "pgvector: Open-source vector similarity search for Postgres." https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector
MIT License - see LICENSE for details.