diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index d5df7888d1cb2..2ac59b7cd4a4e 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -10,12 +10,12 @@
[](https://github.com/cube-js/cube/actions?query=workflow%3ABuild+branch%3Amaster)
[](https://app.fossa.io/projects/git%2Bgithub.com%2Fcube-js%2Fcube.js?ref=badge_shield)
-__Cube Core is an open-source semantic layer.__ Cube Core can be used to build embedded analytics in your applications or create your own business intelligence tool. Cube Core is headless and comes with multiple APIs for embedded analytics and BI: REST, GraphQL, and SQL.
+__Cube Core is an open-source semantic layer.__ Cube Core can be used to build embedded analytics in your applications, create your own business intelligence tool or provide context about data to AI agents. Cube Core is headless and comes with multiple APIs for embedded analytics and BI: REST, GraphQL, and SQL.
If you are looking for a fully integrated platform, check out [Cube](https://cube.dev), a modern AI-first business intelligence platform. We use Cube Core to power it.
 @@ -26,13 +26,11 @@ If you are looking for a fully integrated platform, check out [Cube](https://cub
Cube Core was designed to work with all SQL data sources, including cloud data warehouses like Snowflake, Databricks, and BigQuery; query engines like Presto and Amazon Athena; and application databases like Postgres. Cube Core has a built-in relational caching engine to provide sub-second latency and high concurrency for API requests.
-For more details, see the [introduction](https://cube.dev/docs/cubejs-introduction?ref=github-readme) page in our documentation.
-
## Why Cube Core?
Every business intelligence tool relies on a semantic layer as its core engine—a critical component that defines metrics, dimensions, and business logic while abstracting the complexity of underlying data sources. However, most semantic layers are proprietary, tightly coupled to specific BI platforms, and cannot be reused across different applications.
-Cube Core is an open-source project that aims to create an open, modern semantic layer that can be used to power any analytics application, including business intelligence tools and embedded analytics. By decoupling the semantic layer from specific tools and making it accessible through standard APIs, Cube Core enables organizations to define their metrics once and use them everywhere—from custom dashboards to embedded analytics, from data exploration tools to automated reporting systems.
+Cube Core is an open-source project that aims to create an open, modern semantic layer that can be used to power any analytics applications and AI agents. By decoupling the semantic layer from specific tools and making it accessible through standard APIs, Cube Core enables organizations to define their metrics once and use them everywhere—from BI tools to embedded analytics to AI agents.
## Getting Started 🚀
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx
index 658447d2c5e2d..3a99326daa702 100644
--- a/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx
@@ -1,59 +1,20 @@
# Getting started with Cube
-Cube is a cloud-native application, designed to run in a cloud. You can get
-started with Cube in one of two ways:
-- Run Cube in Cube Cloud and use its managed infrastructure and workspace tools.
-- Deploy Cube to your own infrastructure with Docker.
-
-## Getting started with Cube Cloud
-
-**We recommend using [Cube Cloud][cube-cloud], our managed platform for Cube.**
-It's the easiest way to build, test, deploy, and manage Cube projects and
-it comes with a free tier for development and proof-of-concept projects.
-
-Cube Cloud provides [managed infrastructure][ref-infrastructure] and
-[workspace tools][ref-workspace], including features such as collaboration
-for teams, a web-based data model editor, synchronization with BI tools,
-auto-scaling, and observability.
-
-Please get started with the following guides, tailored for Snowflake and
-Databricks users. You may find them insightful even if you
-have one of many other supported [data sources][ref-data-sources].
+It's easy to get started with Cube—just click the button below and create your free account. Once your account is created, you can connect your data source or use our demo deployment. AI will build your initial semantic model, and you'll be able to use Cube features such as analytics chat, workbooks, dashboards, and Agentic IDE.
-
-
-
-Alternatively, you can explore Cube Cloud on your own or learn by example
-in a demo deployment:
-
-
-
-
## Getting started with Cube Core
-Cube Core is packaged and distributed as Docker images that can be run in
-a containerized environment. You can run Cube Core on your own
-infrastructure with Docker.
+Cube Core is a headless, open-source semantic layer that powers the Cube Business Intelligence Platform. While Cube Core lacks frontend and AI features, you can use it to power your own embedded analytics or build your own AI agent or BI tool.
+
+Cube Core is packaged and distributed as Docker images that can be run in a containerized environment. You can run Cube Core on your own infrastructure with Docker.
-## Migrating from Cube Core to Cube Cloud
+## Migrating from Cube Core to Cube
-Cube Cloud supports several ways for importing existing Cube projects:
+Cube Cloud supports several ways to import existing Cube projects:
- [Import a GitHub repository](/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core/import-github-repository)
- [Import a GitLab repository](/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core/import-gitlab-repository-via-ssh)
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js
index 5ba4d4db02d1d..21d3e185152e3 100644
--- a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js
@@ -1,6 +1,20 @@
module.exports = {
- "cloud": "Cube Cloud and Snowflake",
- "databricks": "Cube Cloud and Databricks",
+ "connect-your-data": "Connect your data",
+ "use-analytics-chat": "Use analytics chat",
+ "create-workbooks-and-dashboards": "Create workbooks and dashboards",
+ "develop-in-ide": "Develop in IDE",
+ "embed-analytics": "Embed analytics",
"core": "Cube Core",
- "migrate-from-core": "Migrate from Cube Core"
+ "cloud": {
+ title: "Cube Cloud and Snowflake",
+ display: "hidden"
+ },
+ "databricks": {
+ title: "Cube Cloud and Databricks",
+ display: "hidden"
+ },
+ "migrate-from-core": {
+ title: "Migrate from Cube Core",
+ display: "hidden"
+ }
}
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/connect-your-data.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/connect-your-data.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..cbaeac0b5ba7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/connect-your-data.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+# Connect your data
+
+
+
+If you don't have a data source to connect to, you can create a demo deployment to test all Cube features with demo data.
+
+
+
+Cube supports multiple warehouses and databases.
+
+
+
+Once you select your data source, follow the instructions on the connection page.
+
+
+
+## AI builds initial semantic model
+
+Select what tables you'd like to use in your initial semantic model and let AI build it.
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/create-workbooks-and-dashboards.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/create-workbooks-and-dashboards.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..4601a174f3b6a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/create-workbooks-and-dashboards.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+# Create workbooks and dashboards
+
+Workbooks are places to curate and organize your analysis. You can create multiple reports using tabs, each focusing on different aspects of your data.
+
+## Create a new workbook
+
+You can create a new workbook in two ways:
+
+- Click the **New Workbook** button on the home page or on the workbooks page
+- Open **Explore** from Analytics Chat, then convert that exploration into a workbook
+
+## Organize analysis with tabs
+
+Use tabs within a workbook to create different reports. Each tab can contain its own analysis, allowing you to explore various aspects of your data and organize multiple insights in one place. The AI agent can help you build analysis in workbook tabs, creating queries and visualizations based on your questions.
+
+
+
+## Share with dashboards
+
+Once you're ready to share your work, you can turn workbooks into [dashboards][ref-dashboards] to organize reports into shareable artifacts. Dashboards let you select and organize reports from your workbooks into polished views for your team and stakeholders. The AI agent can help you create dashboards, manage layout, add filters, and more.
+
+
+Dashboards can be published to make them accessible to your team. Published dashboards provide stakeholders with direct access to the insights that matter most.
+
+[ref-dashboards]: /product/presentation/dashboards
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/develop-in-ide.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/develop-in-ide.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..02a33d866e01b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/develop-in-ide.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+# Develop in IDE
+
+The IDE is a place to develop your data model. Cube supports multiple environments based on Git branches, helping you follow software engineering best practices while developing your data model.
+
+## Branch-based development
+
+Cube uses Git branches to create separate environments for development and production. This allows you to safely make changes to your data model without affecting your production environment. When you need to make a change, you can enter development mode or work on a separate branch to test and refine your changes. This isolation ensures that your production data model remains stable while you experiment and iterate.
+
+
+
+## Commit and push to production
+
+When your changes are ready, you can commit and push them to your production branch. The IDE helps manage this entire process without requiring you to know how Git and version control work in detail. You can save changes, commit them, and merge into production—all from within the IDE interface.
+
+## AI-assisted development
+
+The IDE includes an AI agent that helps you create data models from scratch and make changes to existing data models. Simply describe what you want to build or modify, and the AI agent will assist you in implementing the changes.
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/embed-analytics.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/embed-analytics.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..574b3b53beb32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/embed-analytics.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+# Embed analytics
+
+Cube offers rich options for embedded analytics. You can embed [dashboards][ref-dashboards] and [analytics chat][ref-analytics-chat] as iframes, use the [Analytics Chat API][ref-chat-api] directly to create your own conversational analytics experience, or use [Core Data APIs][ref-core-apis] directly to build custom visualizations, reporting, and dashboarding experiences.
+
+## Embed with iframes
+
+The simplest way to embed Cube content is using iframes. You can embed both dashboards and analytics chat directly into your applications. Cube supports two authentication methods for iframe embedding: [private embedding][ref-private-embedding] for internal use cases and [signed embedding][ref-signed-embedding] for customer-facing applications.
+
+## Use the Chat API
+
+For more control over the conversational analytics experience, you can use the [Analytics Chat API][ref-chat-api] directly. This API-first approach lets you programmatically integrate AI-powered conversations with your data into your applications, giving you full control over the user experience.
+
+## Build custom experiences
+
+If you want complete control over visualizations and user interfaces, you can use [Cube's core APIs][ref-core-apis]—including REST, GraphQL, and SQL APIs—directly. This headless approach enables you to build fully custom visualization, reporting, and dashboarding experiences tailored to your specific needs.
+
+[ref-dashboards]: /product/presentation/dashboards
+[ref-analytics-chat]: /product/exploration/analytics-chat
+[ref-chat-api]: /product/apis-integrations/embed-apis/chat-api
+[ref-core-apis]: /product/apis-integrations/core-data-apis
+[ref-private-embedding]: /product/presentation/embedding/private-embedding
+[ref-signed-embedding]: /product/presentation/embedding/signed-embedding
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..e69de29bb2d1d
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/use-analytics-chat.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/use-analytics-chat.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c179713f1e4b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/use-analytics-chat.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+# Use analytics chat
+
+Once your initial semantic model is ready, you can start using Cube features: analytics chat, workbooks, dashboards, IDE and more.
+
+## Ask analytics questions in chat
+
+On the home page, you can ask AI questions about your data and receive answers as results tables and charts.
+
+
+
+## Explore more
+
+When the AI agent returns a query result in Analytics Chat, click Explore to open that result in an exploration. This allows you to further analyze and visualize the data returned by the AI agent.
+
+## Make changes to data model
+
+The AI agent can create ad-hoc calculations using [Semantic SQL][ref-semantic-sql] directly in the analytics chat. These calculations leverage the full power of SQL to build derived metrics on top of your existing semantic model measures and dimensions. When you need to persist these calculations, simply ask the AI agent to save them to your data model, and it will add them as new measures or dimensions.
+
+[ref-semantic-sql]: /product/introduction#semantic-sql
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx b/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx
index 5ec406f91f069..0a32388704ffd 100644
--- a/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx
+++ b/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx
@@ -1,36 +1,43 @@
+---
+toc: false
+---
+
# Introduction
-Cube is the [agentic analytics](#agentic-analytics) platform built on top of the [open-source semantic layer](#semantic-layer).
+Cube is the business intelligence platform powered by the open-source semantic layer.
-Cube enables AI agents and users to query, explore, and manipulate data models — transforming the semantic layer into a dynamic, governed workspace for generating insights, automating workflows, and building data products.
+Cube uses AI agents to build data models and enable data consumers to perform analysis. Use AI to quickly build semantic layer and fully control the analytics context.
-Cube is a new generation of a BI platform built to be used by both humans and AI agents. It empowers different personas across your organization:
+Cube is a new generation of a business intelligence and embedded analytics platform built to be used by both humans and AI agents. It empowers different personas across your organization:
- **Data Engineers** can quickly curate data models with AI assistance, accelerating the development and maintenance of semantic layers
- **Data Analysts** can perform deep analysis with AI assistance, diving into complex data relationships and patterns
- **Business Users** benefit from workbooks and dashboards that Cube can automatically build and maintain
-- **AI Agents** can be powered by Cube features through MCP and A2A integrations, enabling automated data discovery, analysis, and reporting workflows
-
-With Cube, you can power copilots, automate data workflows, and create interactive analytics experiences—all grounded in a consistent and governed data model.
-## Semantic layer
+## How is Cube different?
At the foundation of Cube's agentic analytics platform is an [open-source semantic layer](https://github.com/cube-js/cube)—the critical infrastructure that enables both AI agents and humans to work with trusted, consistent data.
The semantic layer provides the governed data foundation that makes agentic analytics possible. It organizes data from your cloud data warehouses into centralized, consistent definitions that AI agents can reliably query, explore, and reason about. Without a semantic layer, AI agents would struggle with inconsistent metrics, scattered business logic, and ungoverned data access—making their outputs unreliable and potentially dangerous.
-By establishing a single source of truth for metrics, relationships, and business logic, the semantic layer ensures that AI agents and users work with the same trusted definitions. This consistency is essential for agentic analytics: when an AI agent generates insights or automates workflows, it relies on the semantic layer's data model to understand what metrics mean, how entities relate, and what data users are authorized to access.
+### Semantic SQL
+
+Unlike other tools, Cube AI agents don't query the data warehouse directly. Instead, they query the semantic layer using Semantic SQL, creating a trusted proxy architecture. The semantic layer runtime acts as guardrails between AI agents and your warehouse—all queries must pass through this deterministic runtime, which validates every request and prevents incorrect queries from reaching your data.
-The semantic layer also provides the performance and governance infrastructure needed for agentic workflows. Through caching and pre-aggregations, it ensures AI agents can respond quickly without overwhelming your data warehouse. Through access controls, it guarantees that agents respect the same data security policies as human users.
+Semantic SQL extends Postgres-compatible SQL with the MEASURE function. This architecture lets AI leverage the full power of SQL to build ad-hoc derived calculations on top of existing semantic model calculations, combining flexibility with governance.
-Data engineers use Cube's semantic layer to build and maintain data models, manage access control and caching, and expose data through REST, GraphQL, and SQL APIs—creating the governed foundation that powers agentic analytics experiences, traditional BI tools, and custom data applications.
+Security policies are enforced deterministically at the semantic layer runtime, ensuring consistent access control across all queries.
-### Code-first
+
+
+### Semantic layer architecture
+
+#### Code-first
A code-first approach is essential for both traditional data engineering and agentic analytics. Managing data models, configurations, and policies as code enables the same proven practices that power modern software development: version control for collaboration and code reviews, automated testing and documentation, and established patterns for reusability and maintainability.
@@ -38,8 +45,6 @@ For agentic analytics specifically, a code-first semantic layer creates new poss
Everything within Cube—from configurations to data models to access control policies—is managed through code. This foundation enables both human data engineers and AI agents to collaborate on building and maintaining the semantic layer that powers agentic analytics.
-### Four pillars of semantic layer
-
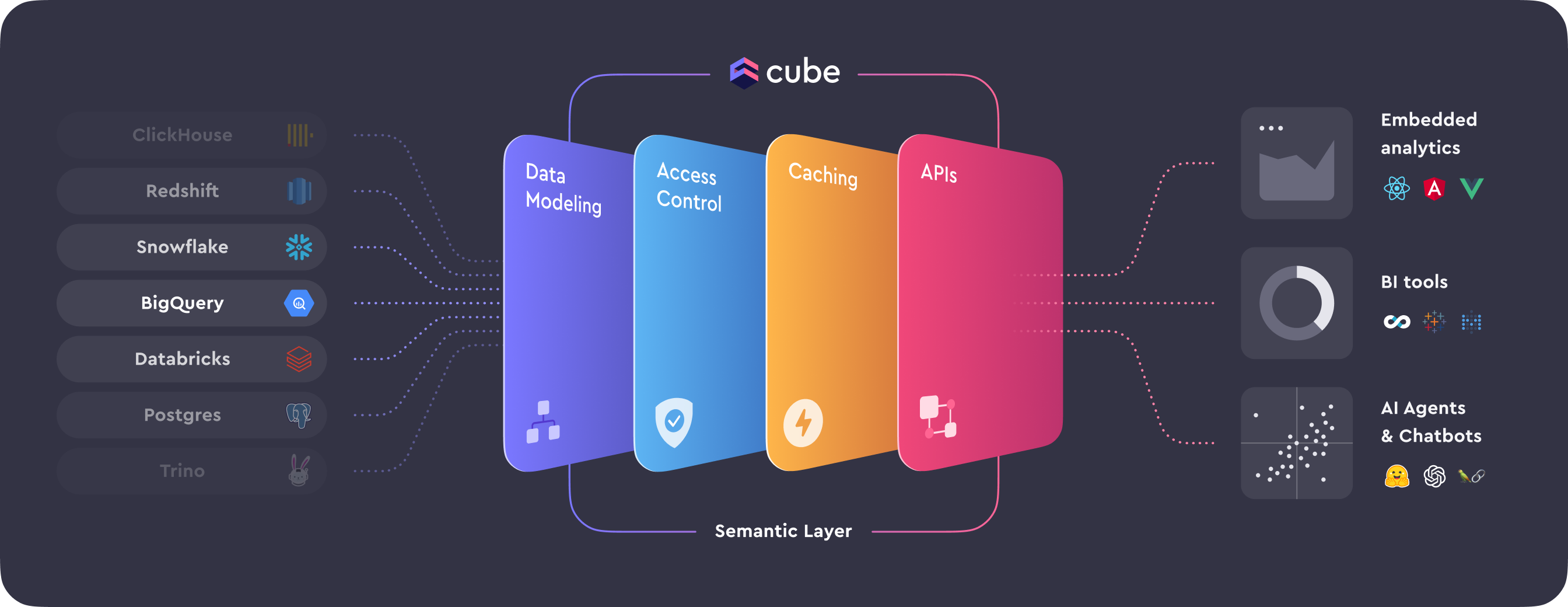
The semantic layer that powers Cube's agentic analytics platform is built on four essential pillars: data modeling, access control, caching, and APIs. Each pillar plays a critical role in enabling AI agents and users to work with data reliably, securely, and efficiently.
#### Data Modeling
diff --git a/docs/theme.config.tsx b/docs/theme.config.tsx
index 6b10df58dfede..c7ad9c2345d60 100644
--- a/docs/theme.config.tsx
+++ b/docs/theme.config.tsx
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ const config: DocsThemeConfig = {
size="s"
href="https://cubecloud.dev/auth/signup?utm_source=docs&utm_medium=site&UTM_Publisher=Cube"
>
- Try Cube for Free
+ Get started for free
)
@@ -26,13 +26,11 @@ If you are looking for a fully integrated platform, check out [Cube](https://cub
Cube Core was designed to work with all SQL data sources, including cloud data warehouses like Snowflake, Databricks, and BigQuery; query engines like Presto and Amazon Athena; and application databases like Postgres. Cube Core has a built-in relational caching engine to provide sub-second latency and high concurrency for API requests.
-For more details, see the [introduction](https://cube.dev/docs/cubejs-introduction?ref=github-readme) page in our documentation.
-
## Why Cube Core?
Every business intelligence tool relies on a semantic layer as its core engine—a critical component that defines metrics, dimensions, and business logic while abstracting the complexity of underlying data sources. However, most semantic layers are proprietary, tightly coupled to specific BI platforms, and cannot be reused across different applications.
-Cube Core is an open-source project that aims to create an open, modern semantic layer that can be used to power any analytics application, including business intelligence tools and embedded analytics. By decoupling the semantic layer from specific tools and making it accessible through standard APIs, Cube Core enables organizations to define their metrics once and use them everywhere—from custom dashboards to embedded analytics, from data exploration tools to automated reporting systems.
+Cube Core is an open-source project that aims to create an open, modern semantic layer that can be used to power any analytics applications and AI agents. By decoupling the semantic layer from specific tools and making it accessible through standard APIs, Cube Core enables organizations to define their metrics once and use them everywhere—from BI tools to embedded analytics to AI agents.
## Getting Started 🚀
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx
index 658447d2c5e2d..3a99326daa702 100644
--- a/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started.mdx
@@ -1,59 +1,20 @@
# Getting started with Cube
-Cube is a cloud-native application, designed to run in a cloud. You can get
-started with Cube in one of two ways:
-- Run Cube in Cube Cloud and use its managed infrastructure and workspace tools.
-- Deploy Cube to your own infrastructure with Docker.
-
-## Getting started with Cube Cloud
-
-**We recommend using [Cube Cloud][cube-cloud], our managed platform for Cube.**
-It's the easiest way to build, test, deploy, and manage Cube projects and
-it comes with a free tier for development and proof-of-concept projects.
-
-Cube Cloud provides [managed infrastructure][ref-infrastructure] and
-[workspace tools][ref-workspace], including features such as collaboration
-for teams, a web-based data model editor, synchronization with BI tools,
-auto-scaling, and observability.
-
-Please get started with the following guides, tailored for Snowflake and
-Databricks users. You may find them insightful even if you
-have one of many other supported [data sources][ref-data-sources].
+It's easy to get started with Cube—just click the button below and create your free account. Once your account is created, you can connect your data source or use our demo deployment. AI will build your initial semantic model, and you'll be able to use Cube features such as analytics chat, workbooks, dashboards, and Agentic IDE.
-
-
-
-Alternatively, you can explore Cube Cloud on your own or learn by example
-in a demo deployment:
-
-
-
-
## Getting started with Cube Core
-Cube Core is packaged and distributed as Docker images that can be run in
-a containerized environment. You can run Cube Core on your own
-infrastructure with Docker.
+Cube Core is a headless, open-source semantic layer that powers the Cube Business Intelligence Platform. While Cube Core lacks frontend and AI features, you can use it to power your own embedded analytics or build your own AI agent or BI tool.
+
+Cube Core is packaged and distributed as Docker images that can be run in a containerized environment. You can run Cube Core on your own infrastructure with Docker.
-## Migrating from Cube Core to Cube Cloud
+## Migrating from Cube Core to Cube
-Cube Cloud supports several ways for importing existing Cube projects:
+Cube Cloud supports several ways to import existing Cube projects:
- [Import a GitHub repository](/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core/import-github-repository)
- [Import a GitLab repository](/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core/import-gitlab-repository-via-ssh)
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js
index 5ba4d4db02d1d..21d3e185152e3 100644
--- a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/_meta.js
@@ -1,6 +1,20 @@
module.exports = {
- "cloud": "Cube Cloud and Snowflake",
- "databricks": "Cube Cloud and Databricks",
+ "connect-your-data": "Connect your data",
+ "use-analytics-chat": "Use analytics chat",
+ "create-workbooks-and-dashboards": "Create workbooks and dashboards",
+ "develop-in-ide": "Develop in IDE",
+ "embed-analytics": "Embed analytics",
"core": "Cube Core",
- "migrate-from-core": "Migrate from Cube Core"
+ "cloud": {
+ title: "Cube Cloud and Snowflake",
+ display: "hidden"
+ },
+ "databricks": {
+ title: "Cube Cloud and Databricks",
+ display: "hidden"
+ },
+ "migrate-from-core": {
+ title: "Migrate from Cube Core",
+ display: "hidden"
+ }
}
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/connect-your-data.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/connect-your-data.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..cbaeac0b5ba7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/connect-your-data.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+# Connect your data
+
+
+
+If you don't have a data source to connect to, you can create a demo deployment to test all Cube features with demo data.
+
+
+
+Cube supports multiple warehouses and databases.
+
+
+
+Once you select your data source, follow the instructions on the connection page.
+
+
+
+## AI builds initial semantic model
+
+Select what tables you'd like to use in your initial semantic model and let AI build it.
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/create-workbooks-and-dashboards.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/create-workbooks-and-dashboards.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..4601a174f3b6a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/create-workbooks-and-dashboards.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+# Create workbooks and dashboards
+
+Workbooks are places to curate and organize your analysis. You can create multiple reports using tabs, each focusing on different aspects of your data.
+
+## Create a new workbook
+
+You can create a new workbook in two ways:
+
+- Click the **New Workbook** button on the home page or on the workbooks page
+- Open **Explore** from Analytics Chat, then convert that exploration into a workbook
+
+## Organize analysis with tabs
+
+Use tabs within a workbook to create different reports. Each tab can contain its own analysis, allowing you to explore various aspects of your data and organize multiple insights in one place. The AI agent can help you build analysis in workbook tabs, creating queries and visualizations based on your questions.
+
+
+
+## Share with dashboards
+
+Once you're ready to share your work, you can turn workbooks into [dashboards][ref-dashboards] to organize reports into shareable artifacts. Dashboards let you select and organize reports from your workbooks into polished views for your team and stakeholders. The AI agent can help you create dashboards, manage layout, add filters, and more.
+
+
+Dashboards can be published to make them accessible to your team. Published dashboards provide stakeholders with direct access to the insights that matter most.
+
+[ref-dashboards]: /product/presentation/dashboards
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/develop-in-ide.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/develop-in-ide.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..02a33d866e01b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/develop-in-ide.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+# Develop in IDE
+
+The IDE is a place to develop your data model. Cube supports multiple environments based on Git branches, helping you follow software engineering best practices while developing your data model.
+
+## Branch-based development
+
+Cube uses Git branches to create separate environments for development and production. This allows you to safely make changes to your data model without affecting your production environment. When you need to make a change, you can enter development mode or work on a separate branch to test and refine your changes. This isolation ensures that your production data model remains stable while you experiment and iterate.
+
+
+
+## Commit and push to production
+
+When your changes are ready, you can commit and push them to your production branch. The IDE helps manage this entire process without requiring you to know how Git and version control work in detail. You can save changes, commit them, and merge into production—all from within the IDE interface.
+
+## AI-assisted development
+
+The IDE includes an AI agent that helps you create data models from scratch and make changes to existing data models. Simply describe what you want to build or modify, and the AI agent will assist you in implementing the changes.
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/embed-analytics.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/embed-analytics.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..574b3b53beb32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/embed-analytics.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+# Embed analytics
+
+Cube offers rich options for embedded analytics. You can embed [dashboards][ref-dashboards] and [analytics chat][ref-analytics-chat] as iframes, use the [Analytics Chat API][ref-chat-api] directly to create your own conversational analytics experience, or use [Core Data APIs][ref-core-apis] directly to build custom visualizations, reporting, and dashboarding experiences.
+
+## Embed with iframes
+
+The simplest way to embed Cube content is using iframes. You can embed both dashboards and analytics chat directly into your applications. Cube supports two authentication methods for iframe embedding: [private embedding][ref-private-embedding] for internal use cases and [signed embedding][ref-signed-embedding] for customer-facing applications.
+
+## Use the Chat API
+
+For more control over the conversational analytics experience, you can use the [Analytics Chat API][ref-chat-api] directly. This API-first approach lets you programmatically integrate AI-powered conversations with your data into your applications, giving you full control over the user experience.
+
+## Build custom experiences
+
+If you want complete control over visualizations and user interfaces, you can use [Cube's core APIs][ref-core-apis]—including REST, GraphQL, and SQL APIs—directly. This headless approach enables you to build fully custom visualization, reporting, and dashboarding experiences tailored to your specific needs.
+
+[ref-dashboards]: /product/presentation/dashboards
+[ref-analytics-chat]: /product/exploration/analytics-chat
+[ref-chat-api]: /product/apis-integrations/embed-apis/chat-api
+[ref-core-apis]: /product/apis-integrations/core-data-apis
+[ref-private-embedding]: /product/presentation/embedding/private-embedding
+[ref-signed-embedding]: /product/presentation/embedding/signed-embedding
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/migrate-from-core.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..e69de29bb2d1d
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/getting-started/use-analytics-chat.mdx b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/use-analytics-chat.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c179713f1e4b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/pages/product/getting-started/use-analytics-chat.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+# Use analytics chat
+
+Once your initial semantic model is ready, you can start using Cube features: analytics chat, workbooks, dashboards, IDE and more.
+
+## Ask analytics questions in chat
+
+On the home page, you can ask AI questions about your data and receive answers as results tables and charts.
+
+
+
+## Explore more
+
+When the AI agent returns a query result in Analytics Chat, click Explore to open that result in an exploration. This allows you to further analyze and visualize the data returned by the AI agent.
+
+## Make changes to data model
+
+The AI agent can create ad-hoc calculations using [Semantic SQL][ref-semantic-sql] directly in the analytics chat. These calculations leverage the full power of SQL to build derived metrics on top of your existing semantic model measures and dimensions. When you need to persist these calculations, simply ask the AI agent to save them to your data model, and it will add them as new measures or dimensions.
+
+[ref-semantic-sql]: /product/introduction#semantic-sql
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx b/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx
index 5ec406f91f069..0a32388704ffd 100644
--- a/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx
+++ b/docs/pages/product/introduction.mdx
@@ -1,36 +1,43 @@
+---
+toc: false
+---
+
# Introduction
-Cube is the [agentic analytics](#agentic-analytics) platform built on top of the [open-source semantic layer](#semantic-layer).
+Cube is the business intelligence platform powered by the open-source semantic layer.
-Cube enables AI agents and users to query, explore, and manipulate data models — transforming the semantic layer into a dynamic, governed workspace for generating insights, automating workflows, and building data products.
+Cube uses AI agents to build data models and enable data consumers to perform analysis. Use AI to quickly build semantic layer and fully control the analytics context.
-Cube is a new generation of a BI platform built to be used by both humans and AI agents. It empowers different personas across your organization:
+Cube is a new generation of a business intelligence and embedded analytics platform built to be used by both humans and AI agents. It empowers different personas across your organization:
- **Data Engineers** can quickly curate data models with AI assistance, accelerating the development and maintenance of semantic layers
- **Data Analysts** can perform deep analysis with AI assistance, diving into complex data relationships and patterns
- **Business Users** benefit from workbooks and dashboards that Cube can automatically build and maintain
-- **AI Agents** can be powered by Cube features through MCP and A2A integrations, enabling automated data discovery, analysis, and reporting workflows
-
-With Cube, you can power copilots, automate data workflows, and create interactive analytics experiences—all grounded in a consistent and governed data model.
-## Semantic layer
+## How is Cube different?
At the foundation of Cube's agentic analytics platform is an [open-source semantic layer](https://github.com/cube-js/cube)—the critical infrastructure that enables both AI agents and humans to work with trusted, consistent data.
The semantic layer provides the governed data foundation that makes agentic analytics possible. It organizes data from your cloud data warehouses into centralized, consistent definitions that AI agents can reliably query, explore, and reason about. Without a semantic layer, AI agents would struggle with inconsistent metrics, scattered business logic, and ungoverned data access—making their outputs unreliable and potentially dangerous.
-By establishing a single source of truth for metrics, relationships, and business logic, the semantic layer ensures that AI agents and users work with the same trusted definitions. This consistency is essential for agentic analytics: when an AI agent generates insights or automates workflows, it relies on the semantic layer's data model to understand what metrics mean, how entities relate, and what data users are authorized to access.
+### Semantic SQL
+
+Unlike other tools, Cube AI agents don't query the data warehouse directly. Instead, they query the semantic layer using Semantic SQL, creating a trusted proxy architecture. The semantic layer runtime acts as guardrails between AI agents and your warehouse—all queries must pass through this deterministic runtime, which validates every request and prevents incorrect queries from reaching your data.
-The semantic layer also provides the performance and governance infrastructure needed for agentic workflows. Through caching and pre-aggregations, it ensures AI agents can respond quickly without overwhelming your data warehouse. Through access controls, it guarantees that agents respect the same data security policies as human users.
+Semantic SQL extends Postgres-compatible SQL with the MEASURE function. This architecture lets AI leverage the full power of SQL to build ad-hoc derived calculations on top of existing semantic model calculations, combining flexibility with governance.
-Data engineers use Cube's semantic layer to build and maintain data models, manage access control and caching, and expose data through REST, GraphQL, and SQL APIs—creating the governed foundation that powers agentic analytics experiences, traditional BI tools, and custom data applications.
+Security policies are enforced deterministically at the semantic layer runtime, ensuring consistent access control across all queries.
-### Code-first
+
+
+### Semantic layer architecture
+
+#### Code-first
A code-first approach is essential for both traditional data engineering and agentic analytics. Managing data models, configurations, and policies as code enables the same proven practices that power modern software development: version control for collaboration and code reviews, automated testing and documentation, and established patterns for reusability and maintainability.
@@ -38,8 +45,6 @@ For agentic analytics specifically, a code-first semantic layer creates new poss
Everything within Cube—from configurations to data models to access control policies—is managed through code. This foundation enables both human data engineers and AI agents to collaborate on building and maintaining the semantic layer that powers agentic analytics.
-### Four pillars of semantic layer
-
The semantic layer that powers Cube's agentic analytics platform is built on four essential pillars: data modeling, access control, caching, and APIs. Each pillar plays a critical role in enabling AI agents and users to work with data reliably, securely, and efficiently.
#### Data Modeling
diff --git a/docs/theme.config.tsx b/docs/theme.config.tsx
index 6b10df58dfede..c7ad9c2345d60 100644
--- a/docs/theme.config.tsx
+++ b/docs/theme.config.tsx
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ const config: DocsThemeConfig = {
size="s"
href="https://cubecloud.dev/auth/signup?utm_source=docs&utm_medium=site&UTM_Publisher=Cube"
>
- Try Cube for Free
+ Get started for free
)